Table of Contents
Jamini Roy (1887-1972)
As early as the 1930s, Jamini Roy had anticipated the current vogue amongst the artists to draw upon folk-art in fashioning artwork.
He attempted to create a distinct indigenous style in seeking inspiration from folk-art traditions as against the elitist approach of the Bengal School.
He found a quality of freshness, directness, and robustness in the artistic spirit that still survived in the scrolls, the bazaar paintings of Kalighat, in the Puja images, in toys and dolls and the hordes of artifacts created for rituals—all synthesized with the visual effects of kanthas and alpanas.

He abandoned his interest in portraiture in oils and the ‘wistful sentimentality’ of Abanindranath’s style after 1910.
He was attracted to the folk- art sources, adopting not only the freest possible manner, characteristic of native folk arts, to shape the figures in his works, but also formal ideas from Orissan and Jain manuscript illustrations of the medieval period.
After the mid-1920s he adopted an increasing use of firm and majestic curves and simple forms. He also changed his palette to mineral and vegetable dyes popularly used in villages, so as to fully identify with the village ethos.
His style, however, gradually became more decorative than poetic or sensuous. He moved away from Kalighat, although he retained some of its characteristics like the large eyes and the oval faces.
In some of his works Of the early 1930s, the stress is on the vertical rigid forms reminiscent of Byzantine icon paintings.
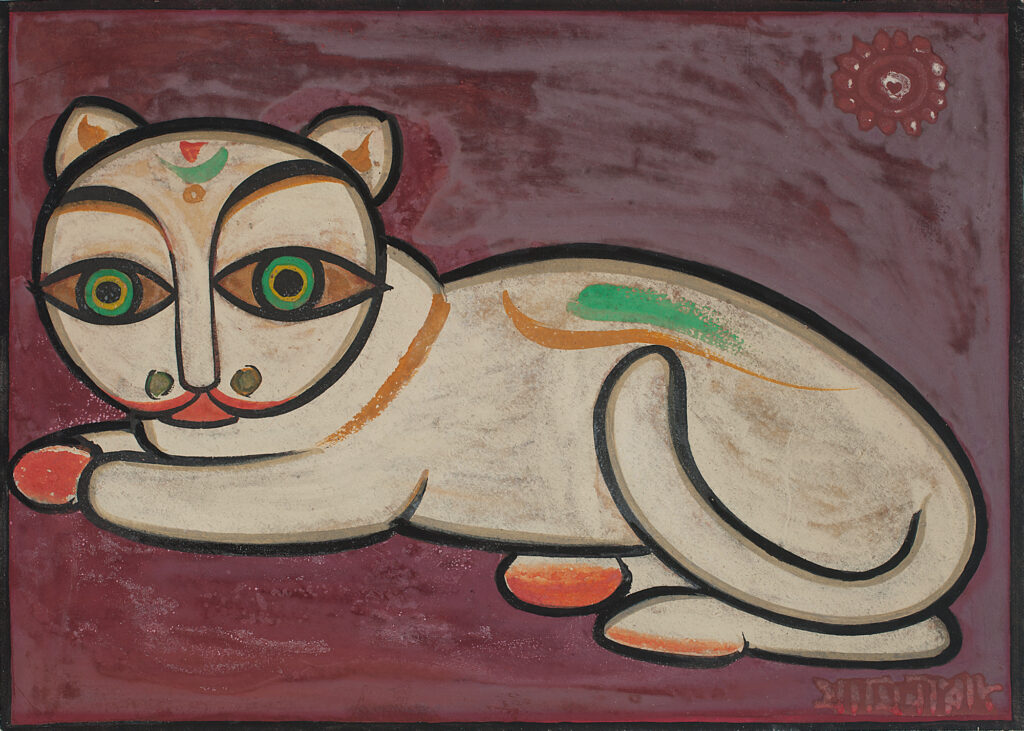
His paintings on the theme of Christ and the satirical paintings of animals, like those of cats with protruding eyes, clearly show the influence of the Jain School.
But, by and large, his paintings are marked by the conventional features of the native folk paintings, i.e. the flattening out of design in-depth, and of voluminous and otherwise massive forms, by omitting light and shade, and use of pure and positive colors in the interaction of their tonal quality and strength.
Jamini Roy’s paintings are a sheer expression of rhythmic lines drawn with curved and elliptic sweeps that define the robust forms of his figures.
He seems to be subordinating everything to the repetitive decorative rhythm in his panel pictures but not in his sketches, some of which are powerful spontaneous expressions.
He added an element of subtlety and sophistication to the simplistic painting of Kalighat, resulting in a strongly individualistic style.
One may wonder why Jamini Roy adopted a style based on folk-art, which, as is well known, he did after a great deal of heartsearching.
Starting his career as a portrait painter in the Western academic tradition and later experimenting with impressionism, he, subsequently discontinued both.
And though the Bengal School was then in the ascendant, he found it too eclectic to be attracted to it.
To overcome this stalemate in the art scene of that time, he strove to strike a new path by turning to native folk-art traditions wherein he discovered the art impulses and genius of his own people.
He, however, did not foresee that the folk-art style he adopted would, in course of time, lead him into a blind alley.
For, unfortunately, his enthusiastic endeavor to strive for Indianness resulted in a ‘factory’ producing Jamini Roys for the elite.
Though artistic control plays a quiet but crucial role in Jamini Roy’s paintings, it raises questions about the significance of creativity in art.
In his search for finding an identity, he styled his artistic activities as a ‘Patua’—the Bengal folk painter. For, he compared his free repetitious approach to that of the ‘Patua’.
Jamini Roy’s stimulus-response model is based on emotionally charged and decorative religious content which, though necessary, is not sufficient for creative expression.
Mere sensation ‘furnishes’ the mind with nothing whatsoever; it leaves no legible character on the ‘white paper’ within us.
For, art is an expression of a totally imaginative creative experience. How- ever, Jamini Roy’s art had nationalistic significance, especially when India was trying to free itself from the clutches of the political and cultural influences of the West.
No one, perhaps, knows with certainty whether Jamini Roy was heading in the right direction; for no one has subsequently followed his approach or style concertedly.
How far his explorations of the aesthetic norms of folk- art were successful in reviving the spirit of indigenous art traditions is a debatable question.
And how valid are the aesthetic norms of bygone days for artistic expression today, especially when the present-day artist faces a vast array of material, styles, and traditions all of which are equally internationally valid? Perhaps time only will decide whether Jamini Roy’s pursuit of artistic labor was successful or not.
Be that as it may, we must remember that Jamini Roy was the first artist to prominently and creatively use folk-art at a time when more and more Indian artists were attracted to alien art forms.
Here are some of Jamini Roy’s famous paintings, including their year, media, and name:
| Painting Name | Year | Media |
|---|---|---|
| Bride and Two Companions | 1940s | Tempera on Cardboard |
| Krishna and Balarama | 1940s | Tempera on Paper |
| Mother and Child | 1940s | Tempera on Cloth |
| Three Pujarinis | 1950s | Tempera on Board |
| Santal Boy with Drum | 1935 | Tempera on Canvas |
| Gopini | 1940s | Tempera on Paper |
| St. Ann and the Blessed Virgin | 1945 | Tempera on Canvas |
| Cats Sharing a Prawn | 1940s | Tempera on Canvas |
| Ravana, Sita, and Jatayu | 1940s | Tempera on Cloth |
| Ramayana Series | 1940s | Tempera on Paper |
| Queen on Tiger | 1930s | Tempera on Paper |
| Makara and a Flock of Fish | 1940s | Tempera on Board |
| Radha and Krishna | 1940s | Tempera on Cloth |
| Seated Woman with Hookah | 1940s | Tempera on Board |
| Chaitanya and His Followers | 1940s | Tempera on Cloth |
| Woman in White Sari | 1940s | Tempera on Canvas |
| Blue Krishna with Gopis | 1940s | Tempera on Board |
| Woman Holding a Lotus | 1950s | Tempera on Canvas |
| Ganesh Janani | 1940s | Tempera on Cloth |
| Dancing Ganesha | 1940s | Tempera on Board |
Jamini Roy was known for his use of earthy colors, bold outlines, and influence from folk art, especially Kalighat paintings.
Chart of Jamini Roy’s paintings from the 1930s, including their year, media, and name:
| Painting Name | Year | Media |
|---|---|---|
| Queen on Tiger | 1930s | Tempera on Paper |
| Santal Boy with Drum | 1935 | Tempera on Canvas |
| Woman with Pitcher | 1930s | Tempera on Board |
| Seated Woman in Sari | 1930s | Tempera on Cloth |
| Mother and Child | 1930s | Tempera on Canvas |
| Woman Holding a Bird | 1930s | Tempera on Paper |
| Dancing Girl | 1930s | Tempera on Board |
| Baul Musician | 1930s | Tempera on Cloth |
| Krishna with Cows | 1930s | Tempera on Paper |
Jamini Roy’s 1930s works marked his transition from Western-style academic painting to a more folk-art-inspired style, using bold lines and natural pigments.
Chart of Jamini Roy’s paintings from the 1940s, including their year, media, and name:
| Painting Name | Year | Media |
|---|---|---|
| Bride and Two Companions | 1940s | Tempera on Cardboard |
| Krishna and Balarama | 1940s | Tempera on Paper |
| Mother and Child | 1940s | Tempera on Cloth |
| Gopini | 1940s | Tempera on Paper |
| Cats Sharing a Prawn | 1940s | Tempera on Canvas |
| Ravana, Sita, and Jatayu | 1940s | Tempera on Cloth |
| Ramayana Series | 1940s | Tempera on Paper |
| Makara and a Flock of Fish | 1940s | Tempera on Board |
| Radha and Krishna | 1940s | Tempera on Cloth |
| Seated Woman with Hookah | 1940s | Tempera on Board |
| Chaitanya and His Followers | 1940s | Tempera on Cloth |
| Woman in White Sari | 1940s | Tempera on Canvas |
| Blue Krishna with Gopis | 1940s | Tempera on Board |
| Ganesh Janani | 1940s | Tempera on Cloth |
| Dancing Ganesha | 1940s | Tempera on Board |
During the 1940s, Jamini Roy fully embraced the folk art style, using natural pigments, simplified forms, and strong outlines inspired by Kalighat paintings.
Chart of Jamini Roy’s paintings from the 1950s, including their year, media, and name:
| Painting Name | Year | Media |
|---|---|---|
| Three Pujarinis | 1950s | Tempera on Board |
| Woman Holding a Lotus | 1950s | Tempera on Canvas |
| Black Horse | 1950s | Tempera on Paper |
| Dancing Figure | 1950s | Tempera on Cloth |
| Mother and Child | 1950s | Tempera on Board |
| Krishna with Flute | 1950s | Tempera on Paper |
| Woman with Flower | 1950s | Tempera on Canvas |
By the 1950s, Jamini Roy had fully established his folk-art-inspired style, using bold colors, simplified figures, and themes from rural life and mythology.
Chart of Jamini Roy’s paintings from the 1960s
Jamini Roy’s artistic peak was between the 1930s and 1950s, and he created fewer notable works in the 1960s. However, here are some of his paintings from that period:
| Painting Name | Year | Media |
|---|---|---|
| Woman with Red Bindi | 1960s | Tempera on Board |
| Mother and Child | 1960s | Tempera on Paper |
| Krishna with Gopis | 1960s | Tempera on Cloth |
| Santal Couple | 1960s | Tempera on Canvas |
| Seated Woman in Blue Sari | 1960s | Tempera on Board |
By the 1960s, Jamini Roy had already received national recognition for his contribution to Indian modern art, and his works continued to reflect folk traditions and mythology.
Jamini Roy continued his folk-art-inspired style in the 1960s, focusing on themes of rural life, mythology, and simplicity. His works during this period maintained his signature use of bold outlines, earthy colors, and tempera on materials like paper, board, and cloth.
Many of his paintings from this time were variations of his earlier works, as he refined and repeated themes such as Mother and Child, Krishna with Gopis, and Santal Life.
In the 1960s, Jamini Roy continued to refine his unique folk-art style, drawing inspiration from traditional Kalighat paintings, Bengali folk art, and rural life. His works from this period followed the same artistic principles he had developed earlier but with more emphasis on simplification, minimalism, and repetition of themes.
Key Features of Jamini Roy’s Art in the 1960s:
- Bold Black Outlines: He used thick, strong outlines to define figures, much like traditional Indian folk art.
- Limited Color Palette: His colors were mostly earthy tones, including ochre, red, blue, green, and white, often made from natural pigments.
- Religious and Folk Themes: He focused on Hindu mythology (Krishna, Radha, Gopis), rural Bengali life (Santal couples, musicians, and dancers), and mother-child relationships.
- Use of Traditional Materials: He avoided oil paints and canvas, preferring tempera on cloth, board, or paper.
- Flat, Two-Dimensional Figures: His figures lacked shading and depth, appearing flat but expressive.
Notable Paintings from the 1960s:
| Painting Name | Media |
|---|---|
| Woman with Red Bindi | Tempera on Board |
| Mother and Child | Tempera on Paper |
| Krishna with Gopis | Tempera on Cloth |
| Santal Couple | Tempera on Canvas |
| Seated Woman in Blue Sari | Tempera on Board |
Even in his later years, Jamini Roy’s art remained deeply connected to Indian traditions, folk culture, and simplicity. His work influenced many modern Indian artists and remains highly valued today.
Jamini Roy’s Artistic Techniques and Influences
Jamini Roy was one of India’s most celebrated modern artists, known for rejecting Western artistic traditions and embracing Indian folk art. His work was deeply influenced by Bengali rural culture, Kalighat paintings, and temple art.
1. Artistic Techniques Used by Jamini Roy
A. Use of Traditional Materials
- He abandoned oil paints and canvas, using tempera (a mixture of pigment and water) on cloth, board, and paper.
- He preferred natural colors made from organic sources, such as:
- Red: From crushed stones and flowers
- Yellow: From turmeric
- Blue: From indigo
- Black: From soot
- White: From crushed shells
B. Simplified, Folk-Inspired Figures
- His figures were flat, two-dimensional, and outlined in bold black lines, much like traditional Kalighat paintings.
- He used minimal details to keep the focus on form and emotion rather than realism.
- The eyes in his paintings were large and expressive, influenced by Indian iconography.
C. Limited Color Palette
- He used earthy and primary colors instead of Western-style shading or realism.
- Colors were applied in flat, unblended areas, creating a striking and bold effect.
D. Repetition of Themes
- Roy painted multiple versions of his subjects, refining them over time.
- His recurring themes included:
- Hindu mythology (Krishna, Radha, Ramayana scenes)
- Mother and child (symbolizing maternal love and Indian motherhood)
- Bengali village life (Santals, musicians, dancers)
- Animals (Cats, horses, owls, and fish)
2. Major Influences on Jamini Roy
A. Kalighat Paintings
- Kalighat paintings originated near the Kalighat Temple in Kolkata and were created by local artisans.
- These paintings had bold lines, vibrant colors, and religious themes, all of which Roy incorporated into his work.
B. Bengali Folk Art and Rural Traditions
- Roy was deeply inspired by Bengali patachitra (scroll paintings) and terracotta temple carvings.
- He painted Santals (an indigenous community) with bright costumes and musical instruments, capturing their lively culture.
C. Ajanta Cave Paintings
- The ancient Ajanta cave murals influenced Roy’s use of flat compositions, elongated figures, and spiritual themes.
D. Western Training and Rejection of Realism
- Initially trained in Western classical painting at the Government College of Art & Craft, Kolkata, Roy mastered European styles.
- However, he rejected realism and Impressionism, turning to Indian folk traditions to create an authentic national art style.
3. Impact of Jamini Roy’s Art
- He was one of the first Indian artists to develop a truly “Indian modern art” style, free from European influences.
- His work was affordable and accessible, making art available beyond the elite class.
- He was awarded the Padma Bhushan (India’s third-highest civilian award) in 1954 for his contribution to art.
- Today, his paintings are highly valued and displayed in major museums, including the National Gallery of Modern Art (NGMA) in New Delhi.
Conclusion
Jamini Roy’s work was a revolution in Indian art, blending tradition with modernity. His use of folk themes, natural colors, bold outlines, and simplified forms made his art timeless and unique.
Read More About Famous Artists:
Somnath Hore, Dhan Raj Bhagat, Ramkinkar Vaij, Arpana Caur, Jai Zharotia, Gogi Saroj Pal, Vivan Sundaram, Manjit Bawa, Jatin Das, Biren De, Gulam Mohammad Sheikh, Arpita Singh, A Ramachandran, Om Prakash, Shanti Dave, Bishamber Khanna, Jagdish Swaminathan, Anjolie Ela Menon, Satish Gujral, G.R. Santosh
- प्राचीन भारतीय कला पर 100 बहुविकल्पीय प्रश्न
 अजंता की गुफाएं 1. अजंता की गुफाएं किस राज्य में स्थित हैं? सही उत्तर: b) … Read more
अजंता की गुफाएं 1. अजंता की गुफाएं किस राज्य में स्थित हैं? सही उत्तर: b) … Read more - ऐतिहासिक कला पर 100 बहुविकल्पीय प्रश्न
 100 multiple choice questions on art history प्राचीन भारतीय कला 1. अजंता की गुफाओं में … Read more
100 multiple choice questions on art history प्राचीन भारतीय कला 1. अजंता की गुफाओं में … Read more - कंदरिया महादेव मंदिर पर 100 बहुविकल्पीय प्रश्न
 सामान्य जानकारी और इतिहास 1. कंदरिया महादेव मंदिर कहाँ स्थित है? सही उत्तर: b) खजुराहो, … Read more
सामान्य जानकारी और इतिहास 1. कंदरिया महादेव मंदिर कहाँ स्थित है? सही उत्तर: b) खजुराहो, … Read more - Make Money Selling AI Art: $3,400 With Free Tools Guide
 Learn how I earned $3,400 in 2 years selling AI art on Etsy and stock … Read more
Learn how I earned $3,400 in 2 years selling AI art on Etsy and stock … Read more - Kangra Chitrakala MCQs – 100 बहुविकल्पीय प्रश्न हिंदी में उत्तर सहित 2026
 कांगड़ा चित्रकला ( Kangra Chitrakala MCQs ) के 100 बहुविकल्पीय प्रश्न उत्तर सहित। इतिहास, विशेषताएं, … Read more
कांगड़ा चित्रकला ( Kangra Chitrakala MCQs ) के 100 बहुविकल्पीय प्रश्न उत्तर सहित। इतिहास, विशेषताएं, … Read more - Pal Shaili – पाल चित्रकला: बौद्ध कला की जानकारी 2026
 पाल चित्रकला (750-1200 ई.) की संपूर्ण जानकारी – नालंदा, विक्रमशिला, बौद्ध पांडुलिपि, ताड़पत्र, धीमान-वीतपाल, विशेषताएं … Read more
पाल चित्रकला (750-1200 ई.) की संपूर्ण जानकारी – नालंदा, विक्रमशिला, बौद्ध पांडुलिपि, ताड़पत्र, धीमान-वीतपाल, विशेषताएं … Read more - पाल चित्रकला – 100 बहुविकल्पीय प्रश्न (MCQs)
 खंड 1: पाल चित्रकला – परिचय और इतिहास (1-20) 1. पाल चित्रकला का समयकाल क्या … Read more
खंड 1: पाल चित्रकला – परिचय और इतिहास (1-20) 1. पाल चित्रकला का समयकाल क्या … Read more - कांगड़ा चित्रकला: पहाड़ी शैली की संपूर्ण जानकारी 2026
 कांगड़ा चित्रकला की संपूर्ण जानकारी – विशेषताएं, इतिहास, विकास, नैनसुख, संसार चंद, राधा-कृष्ण चित्र, गुलेर … Read more
कांगड़ा चित्रकला की संपूर्ण जानकारी – विशेषताएं, इतिहास, विकास, नैनसुख, संसार चंद, राधा-कृष्ण चित्र, गुलेर … Read more - दृश्य संप्रेषण कला: इतिहास, तत्व, आधुनिक अनुप्रयोग और NET/JRF तैयारी
 जानें दृश्य संप्रेषण कला क्या है, इसके तत्व, ऐतिहासिक विकास, आधुनिक डिजिटल अनुप्रयोग, और NET/JRF … Read more
जानें दृश्य संप्रेषण कला क्या है, इसके तत्व, ऐतिहासिक विकास, आधुनिक डिजिटल अनुप्रयोग, और NET/JRF … Read more - ग्राफ़िक डिज़ाइन क्या है? परिभाषा, इतिहास, तत्व, प्रकार, प्रक्रिया | MCQs & NET/JRF प्रश्न
 ग्राफ़िक डिज़ाइन का विस्तृत अध्ययन — अर्थ, परिभाषा, इतिहास, तत्व, सिद्धांत, प्रकार, टाइपोग्राफी, रंग सिद्धांत, … Read more
ग्राफ़िक डिज़ाइन का विस्तृत अध्ययन — अर्थ, परिभाषा, इतिहास, तत्व, सिद्धांत, प्रकार, टाइपोग्राफी, रंग सिद्धांत, … Read more - गुप्तकालीन मूर्तिकला : विशेषताएँ, शैलियाँ, उदाहरण, FAQs और MCQs
 गुप्तकालीन मूर्तिकला पर विस्तृत हिंदी लेख – विशेषताएँ, मथुरा व सारनाथ शैली, बुद्ध-विष्णु-शिव प्रतिमाएँ, FAQs … Read more
गुप्तकालीन मूर्तिकला पर विस्तृत हिंदी लेख – विशेषताएँ, मथुरा व सारनाथ शैली, बुद्ध-विष्णु-शिव प्रतिमाएँ, FAQs … Read more - गुप्तकालीन कला : मूर्तिकला, चित्रकला, वास्तुकला | सम्पूर्ण अध्ययन, MCQs एवं FAQs (हिंदी)
 गुप्तकालीन कला पर विस्तृत अध्ययन—मूर्तिकला, चित्रकला, वास्तुकला एवं धातु कला का संपूर्ण विश्लेषण। TGT/PGT, UPSC, … Read more
गुप्तकालीन कला पर विस्तृत अध्ययन—मूर्तिकला, चित्रकला, वास्तुकला एवं धातु कला का संपूर्ण विश्लेषण। TGT/PGT, UPSC, … Read more - गुप्तकालीन कला: स्वर्ण युग की संपूर्ण जानकारी 2026
 गुप्तकालीन कला की संपूर्ण जानकारी हिंदी में। भारतीय कला के स्वर्ण युग (320-550 ई.) की … Read more
गुप्तकालीन कला की संपूर्ण जानकारी हिंदी में। भारतीय कला के स्वर्ण युग (320-550 ई.) की … Read more - ६. वर्णिका भंग (रंगों का मिश्रण और प्रयोग)
 Color blending (mixing and using colors) परिभाषा और सार वर्णिका भंग संस्कृत के ‘वर्णिका’ (रंग) और … Read more
Color blending (mixing and using colors) परिभाषा और सार वर्णिका भंग संस्कृत के ‘वर्णिका’ (रंग) और … Read more - ५. सादृश्य (समानता और यथार्थता)
 परिभाषा और सार सादृश्य संस्कृत के ‘स’ (साथ) और ‘दृश्य’ (दिखाई देना) से बना है, जिसका … Read more
परिभाषा और सार सादृश्य संस्कृत के ‘स’ (साथ) और ‘दृश्य’ (दिखाई देना) से बना है, जिसका … Read more - ४. लावण्य योजना (सौंदर्य और अनुग्रह)
 परिभाषा और सार लावण्य योजना चित्रकला का वह दिव्य और सूक्ष्म तत्व है जो चित्र में … Read more
परिभाषा और सार लावण्य योजना चित्रकला का वह दिव्य और सूक्ष्म तत्व है जो चित्र में … Read more - ३. भाव (भावनाओं की अभिव्यक्ति)
 परिभाषा और महत्व भाव चित्रकला का सबसे महत्वपूर्ण, प्राणवान और हृदयस्पर्शी तत्व है। संस्कृत में ‘भाव’ … Read more
परिभाषा और महत्व भाव चित्रकला का सबसे महत्वपूर्ण, प्राणवान और हृदयस्पर्शी तत्व है। संस्कृत में ‘भाव’ … Read more - २. प्रमाण (माप और अनुपात)
 परिभाषा और मूल सिद्धांत प्रमाण शब्द संस्कृत की ‘प्र’ (उत्तम) और ‘माण’ (माप) से बना है, … Read more
परिभाषा और मूल सिद्धांत प्रमाण शब्द संस्कृत की ‘प्र’ (उत्तम) और ‘माण’ (माप) से बना है, … Read more - भारतीय चित्रकला के अंग (रूपभेद)
 रूपभेद (रूपों की विविधता) Morphological variation (diversity of forms) परिभाषा और मूल अवधारणा रूपभेद चित्रकला का … Read more
रूपभेद (रूपों की विविधता) Morphological variation (diversity of forms) परिभाषा और मूल अवधारणा रूपभेद चित्रकला का … Read more - भारतीय चित्रकला के षड्अंग (छह अंग)
 The six limbs (or principles) of Indian painting भारतीय चित्रकला की परंपरा अत्यंत प्राचीन और … Read more
The six limbs (or principles) of Indian painting भारतीय चित्रकला की परंपरा अत्यंत प्राचीन और … Read more - कला / चित्रकला की प्रमुख विशेषताएँ : 100 MCQs (हिंदी)Key Features of Art/Painting: 100 MCQs (Hindi) नीचे कला / चित्रकला की प्रमुख विशेषताओं पर आधारित 100 वस्तुनिष्ठ … Read more
- Topic-wise MCQs (रेखा, रंग, सौंदर्य, भाव)Topic-wise MCQs (Lines, Colors, Beauty, Emotions) Topic–1 : रेखा (Line) — 25 MCQs 1. चित्रकला … Read more
- कला / चित्रकला की प्रमुख विशेषताएँ : MCQs (हिंदी)Key features of art/painting: MCQs (Hindi) 1. कला का मूल तत्व क्या है? A) अनुकरणB) … Read more
- the field of art | कला का क्षेत्रकला मानव सभ्यता की सबसे प्राचीन और महत्वपूर्ण अभिव्यक्तियों में से एक है। यह न … Read more
- कला के प्रमुख तत्व: सौंदर्य, अभिव्यक्ति, सृजनात्मकता और कल्पना
 elements of art are: beauty, expression, creativity, and imagination. प्रस्तावना कला मानव सभ्यता की सबसे … Read more
elements of art are: beauty, expression, creativity, and imagination. प्रस्तावना कला मानव सभ्यता की सबसे … Read more - कला शिक्षण के उद्देश्य
 प्रस्तावना कला शिक्षण मानव विकास का एक महत्वपूर्ण अंग है जो व्यक्ति के सर्वांगीण विकास … Read more
प्रस्तावना कला शिक्षण मानव विकास का एक महत्वपूर्ण अंग है जो व्यक्ति के सर्वांगीण विकास … Read more - कला का अर्थ: B.Ed. के लिए विस्तृत अध्ययन सामग्री
 The meaning of art: Detailed study material for B.Ed. प्रस्तावना कला मानव सभ्यता का अभिन्न … Read more
The meaning of art: Detailed study material for B.Ed. प्रस्तावना कला मानव सभ्यता का अभिन्न … Read more - कला का शाब्दिक और व्यापक अर्थ
 कला का शाब्दिक अर्थ (Literal Meaning) व्युत्पत्ति (Etymology) ‘कला’ शब्द संस्कृत की ‘कला’ धातु से … Read more
कला का शाब्दिक अर्थ (Literal Meaning) व्युत्पत्ति (Etymology) ‘कला’ शब्द संस्कृत की ‘कला’ धातु से … Read more - दृश्य कला: एक विस्तृत अध्ययन
 चित्रकला, मूर्तिकला, वास्तुकला और फोटोग्राफी प्रस्तावना दृश्य कला मानव सभ्यता की सबसे प्राचीन और महत्वपूर्ण … Read more
चित्रकला, मूर्तिकला, वास्तुकला और फोटोग्राफी प्रस्तावना दृश्य कला मानव सभ्यता की सबसे प्राचीन और महत्वपूर्ण … Read more - Types of Art: A Complete Guide कला के प्रकार: एक संपूर्ण मार्गदर्शिका
 प्रस्तावना कला मानव सभ्यता की आत्मा है। यह वह माध्यम है जिसके द्वारा मनुष्य अपनी … Read more
प्रस्तावना कला मानव सभ्यता की आत्मा है। यह वह माध्यम है जिसके द्वारा मनुष्य अपनी … Read more - भारतीय जल रंग चित्रकार: व्यापक परिचय
 जल रंग चित्रकला: कला का नाजुक माध्यम जल रंग चित्रकला को कला की सबसे चुनौतीपूर्ण … Read more
जल रंग चित्रकला: कला का नाजुक माध्यम जल रंग चित्रकला को कला की सबसे चुनौतीपूर्ण … Read more - कला क्या है? (B.Ed. परिप्रेक्ष्य)
 कला मानवता की सबसे मौलिक अभिव्यक्ति के रूपों में से एक है, फिर भी इसे … Read more
कला मानवता की सबसे मौलिक अभिव्यक्ति के रूपों में से एक है, फिर भी इसे … Read more - कला का अर्थ (Kala ka Arth) — एक विस्तृत एवं समग्र अध्ययन
 नीचे लगभग 1000 शब्दों में “कला का अर्थ” विषय पर एक समग्र, परीक्षा-उपयोगी, वर्णनात्मक लेख … Read more
नीचे लगभग 1000 शब्दों में “कला का अर्थ” विषय पर एक समग्र, परीक्षा-उपयोगी, वर्णनात्मक लेख … Read more - कला का अर्थ (Kala ka Arth) — एक समग्र एवं विस्तृत लेख
 भूमिका कला मानव सभ्यता की आत्मा है। जब मनुष्य ने बोलना, सोचना और महसूस करना … Read more
भूमिका कला मानव सभ्यता की आत्मा है। जब मनुष्य ने बोलना, सोचना और महसूस करना … Read more - सर जे.जे. स्कूल ऑफ़ आर्ट, मुंबई: आधुनिक भारतीय कला का उद्गम स्थल।
 परिचय सर जामसेटजी जीजीभॉय स्कूल ऑफ आर्ट (Sir J.J. School of Art), जिसे सामान्यतः जे.जे. … Read more
परिचय सर जामसेटजी जीजीभॉय स्कूल ऑफ आर्ट (Sir J.J. School of Art), जिसे सामान्यतः जे.जे. … Read more - ए. रामचंद्रन: भारतीय समकालीन कला के महान चित्रकार
 प्रारंभिक जीवन और शिक्षा अचुतन रामचंद्रन नायर, जिन्हें ए. रामचंद्रन के नाम से जाना जाता … Read more
प्रारंभिक जीवन और शिक्षा अचुतन रामचंद्रन नायर, जिन्हें ए. रामचंद्रन के नाम से जाना जाता … Read more - अफ्रीकी और अफ्रीकी-अमेरिकी कला: एक व्यापक अध्ययन
 परिचय अफ्रीकी और अफ्रीकी-अमेरिकी कला विश्व की सबसे प्रभावशाली और समृद्ध कला परंपराओं में से … Read more
परिचय अफ्रीकी और अफ्रीकी-अमेरिकी कला विश्व की सबसे प्रभावशाली और समृद्ध कला परंपराओं में से … Read more - सजावटी कला: एक विस्तृत अध्ययन
 परिचय सजावटी कला (Decorative Arts) उन कला रूपों को संदर्भित करती है जो सौंदर्यात्मक और … Read more
परिचय सजावटी कला (Decorative Arts) उन कला रूपों को संदर्भित करती है जो सौंदर्यात्मक और … Read more - सजावटी कला में डिजाइन के मूलभूत तत्व और सिद्धांत
 Fundamental Elements and Principles of Design in Decorative Arts परिचय डिजाइन के मूलभूत तत्व और … Read more
Fundamental Elements and Principles of Design in Decorative Arts परिचय डिजाइन के मूलभूत तत्व और … Read more - अब्दुर रहमान चुगताई: एक व्यापक अध्ययन
 प्रस्तावना अब्दुर रहमान चुगताई (1897-1975) बीसवीं शताब्दी के सबसे महत्वपूर्ण और विशिष्ट दक्षिण एशियाई कलाकारों … Read more
प्रस्तावना अब्दुर रहमान चुगताई (1897-1975) बीसवीं शताब्दी के सबसे महत्वपूर्ण और विशिष्ट दक्षिण एशियाई कलाकारों … Read more - Six Limbs of Indian Painting (Shadanga)
 Short Notes / Revision Notes 📌 Meaning Shadanga = Six Limbs of PaintingThese are the … Read more
Short Notes / Revision Notes 📌 Meaning Shadanga = Six Limbs of PaintingThese are the … Read more - Modern art quiz
 Modern Art Quiz NEXT let currentQuestion = 0; const quizContainer = document.getElementById(“quiz”); const nextBtn = … Read more
Modern Art Quiz NEXT let currentQuestion = 0; const quizContainer = document.getElementById(“quiz”); const nextBtn = … Read more - Art quiz
 Famous Paintings and Artists Quiz NEXT let currentQuestion = 0; const quizContainer = document.getElementById(“quiz”); const … Read more
Famous Paintings and Artists Quiz NEXT let currentQuestion = 0; const quizContainer = document.getElementById(“quiz”); const … Read more - Modern Art Quiz
 Modern Art Quiz NEXT let currentQuestion = 0; const quizContainer = document.getElementById(“quiz”); const nextBtn = … Read more
Modern Art Quiz NEXT let currentQuestion = 0; const quizContainer = document.getElementById(“quiz”); const nextBtn = … Read more - SCULPTURE — 100 MCQs (WITH ANSWERS)
 1. The “Pietà” is sculpted by: A) DonatelloB) MichelangeloC) BerniniD) GhibertiAnswer: B 2. The material … Read more
1. The “Pietà” is sculpted by: A) DonatelloB) MichelangeloC) BerniniD) GhibertiAnswer: B 2. The material … Read more - Ajanta Art Quiz
 Ajanta Art Quiz Restart Quiz let currentQuestion = 0; let score = 0; const quizContainer … Read more
Ajanta Art Quiz Restart Quiz let currentQuestion = 0; let score = 0; const quizContainer … Read more - Mughal Art Quiz
 Mughal Art Quiz Restart Quiz let currentQuestion = 0; let score = 0; const quizContainer … Read more
Mughal Art Quiz Restart Quiz let currentQuestion = 0; let score = 0; const quizContainer … Read more - COLOUR THEORY — 100 MCQs
 1. Primary colours in pigment (RYB) are— A) Red, Yellow, BlueB) Red, Green, BlueC) Cyan, … Read more
1. Primary colours in pigment (RYB) are— A) Red, Yellow, BlueB) Red, Green, BlueC) Cyan, … Read more - Modern Art vs Classical Art Quiz
 Modern Art vs Classical Art Quiz Restart Quiz let currentQuestion = 0; let score = … Read more
Modern Art vs Classical Art Quiz Restart Quiz let currentQuestion = 0; let score = … Read more - Indian Mythology Quiz
 Indian Mythology Quiz Restart Quiz let currentQuestion = 0; let score = 0; const quizContainer … Read more
Indian Mythology Quiz Restart Quiz let currentQuestion = 0; let score = 0; const quizContainer … Read more - PRINTMAKING — 100 MCQs
 1. Printmaking involves creating artworks by— A. Painting directly on canvasB. Carving blocksC. Making multiple … Read more
1. Printmaking involves creating artworks by— A. Painting directly on canvasB. Carving blocksC. Making multiple … Read more - ग्राफिक कलाएं
 ग्राफिक कलाएँ उन छापा-चित्रों (प्रिण्ट्स) से सम्बन्धित हैं जिनमें किसी ‘वस्तु’ की ‘छाप’ के द्वारा … Read more
ग्राफिक कलाएँ उन छापा-चित्रों (प्रिण्ट्स) से सम्बन्धित हैं जिनमें किसी ‘वस्तु’ की ‘छाप’ के द्वारा … Read more - Major Artists of the Mughal Court
 Introduction to Mughal Court Painting When we talk about Indian miniature painting, one name shines … Read more
Introduction to Mughal Court Painting When we talk about Indian miniature painting, one name shines … Read more - Major Artists of the Mughal Court: Legendary Masters Who Defined an Empire
 Major artists of the Mughal court shaped India’s greatest miniature painting tradition, blending Persian finesse with Indian realism under imperial patronage.
Major artists of the Mughal court shaped India’s greatest miniature painting tradition, blending Persian finesse with Indian realism under imperial patronage. - Art Pedagogy & Teaching Methods
 Art education transforms lives by developing creativity, critical thinking, visual literacy, and self-expression. Effective art … Read more
Art education transforms lives by developing creativity, critical thinking, visual literacy, and self-expression. Effective art … Read more - Printmaking: The Art of Multiplicity
 Printmaking stands as one of humanity’s most democratizing art forms—a practice that transforms the singular … Read more
Printmaking stands as one of humanity’s most democratizing art forms—a practice that transforms the singular … Read more - Ancient Tribal Art of Maharashtra
 Maharashtra—a vast state stretching from the Arabian Sea coast through the Deccan plateau to inland … Read more
Maharashtra—a vast state stretching from the Arabian Sea coast through the Deccan plateau to inland … Read more - Tanjore Painting: The Timeless Gold-Leaf Legacy of South Indian Art
 Introduction to Tanjore Painting What Is Tanjore (Thanjavur) Painting? Tanjore painting represents one of India’s … Read more
Introduction to Tanjore Painting What Is Tanjore (Thanjavur) Painting? Tanjore painting represents one of India’s … Read more - General Knowledge of Art & Culture
 Understanding art and culture requires recognizing how creative expression reflects and shapes human experience across time and geography. This knowledge encompasses diverse traditions, movements, cultural contexts, and the interconnections between artistic practice and society.
Understanding art and culture requires recognizing how creative expression reflects and shapes human experience across time and geography. This knowledge encompasses diverse traditions, movements, cultural contexts, and the interconnections between artistic practice and society. - Drawing & Painting Techniques
 Mastering drawing and painting requires understanding fundamental techniques that have been refined over centuries. Whether you’re a beginner or advancing your skills, these core methods form the foundation of visual art.
Mastering drawing and painting requires understanding fundamental techniques that have been refined over centuries. Whether you’re a beginner or advancing your skills, these core methods form the foundation of visual art. - Art History of India: Ancient to Modern
 The artistic heritage of India spans over 5,000 years, reflecting the subcontinent’s rich cultural, religious, … Read more
The artistic heritage of India spans over 5,000 years, reflecting the subcontinent’s rich cultural, religious, … Read more - 80 PAINTING MCQs For TGT/PGT ART
 1. Which painting technique uses pigments mixed with hot wax? A. GouacheB. EncausticC. TemperaD. OilAnswer: … Read more
1. Which painting technique uses pigments mixed with hot wax? A. GouacheB. EncausticC. TemperaD. OilAnswer: … Read more - TGT/PGT ART SCULPTURE – 100 MCQs
 1. The subtractive method of sculpture involves— A. Adding materialB. Removing materialC. CastingD. ModelingAnswer: B … Read more
1. The subtractive method of sculpture involves— A. Adding materialB. Removing materialC. CastingD. ModelingAnswer: B … Read more - ART PEDAGOGY — 100 MCQs
 1. The primary aim of art education is to— A) Train professional artistsB) Develop aesthetic … Read more
1. The primary aim of art education is to— A) Train professional artistsB) Develop aesthetic … Read more - MCQs for TGT / PGT ART (with answers)
 Topic-wise sets (painting, sculpture, pedagogy, colour theory, Indian art) SET 1 — PAINTING (20 MCQs) … Read more
Topic-wise sets (painting, sculpture, pedagogy, colour theory, Indian art) SET 1 — PAINTING (20 MCQs) … Read more - 100 MCQs for TGT / PGT ART (with answers)
 SECTION A — INDIAN ART (1–30) SECTION B — WESTERN ART (31–55) SECTION C — … Read more
SECTION A — INDIAN ART (1–30) SECTION B — WESTERN ART (31–55) SECTION C — … Read more - Kalipada Ghoshal: Master of Bengali Modernism and Tempera Painting
 Kalipada Ghoshal was born on May 17, 1906, in Jodhpur Park, Calcutta (now Kolkata), West Bengal, into a middle-class Bengali family during a period of extraordinary cultural ferment in Bengal. His birth came just one year after the controversial partition of Bengal by the British colonial government, an event that galvanized Bengali cultural and political consciousness and contributed to the Swadeshi movement’s emphasis on indigenous culture and traditions.
Kalipada Ghoshal was born on May 17, 1906, in Jodhpur Park, Calcutta (now Kolkata), West Bengal, into a middle-class Bengali family during a period of extraordinary cultural ferment in Bengal. His birth came just one year after the controversial partition of Bengal by the British colonial government, an event that galvanized Bengali cultural and political consciousness and contributed to the Swadeshi movement’s emphasis on indigenous culture and traditions. - 100 MCQs for TGT/PGT ART
 (Answers provided at the end) SECTION A — INDIAN ART (1–25) SECTION B — WESTERN … Read more
(Answers provided at the end) SECTION A — INDIAN ART (1–25) SECTION B — WESTERN … Read more - Sculpture & Craft Techniques
 Sculpture and craft encompass three-dimensional art forms that transform materials into expressive objects. From ancient clay modeling to contemporary installations, these techniques allow artists to manipulate space, form, and texture in ways unique to physical making.
Sculpture and craft encompass three-dimensional art forms that transform materials into expressive objects. From ancient clay modeling to contemporary installations, these techniques allow artists to manipulate space, form, and texture in ways unique to physical making. - Famous Dancers of India: India’s Legendary Performers Who Transformed the World of Dance
 India’s dance heritage is one of the richest artistic traditions in the world. From temple courtyards to global stages, Indian dancers have carried forward centuries-old cultural practices while shaping new forms of artistic expression.
India’s dance heritage is one of the richest artistic traditions in the world. From temple courtyards to global stages, Indian dancers have carried forward centuries-old cultural practices while shaping new forms of artistic expression. - Famous Dancers of India: Legends Who Shaped the Nation’s Cultural Heritage
 Discover the most famous dancers of India, their contributions, classical dance forms, and lasting legacy. Explore icons of Bharatanatyam, Kathak, Odissi, and more.
Discover the most famous dancers of India, their contributions, classical dance forms, and lasting legacy. Explore icons of Bharatanatyam, Kathak, Odissi, and more. - MCQs – Mughal School of Painting
 1. The Mughal School of Painting developed as a fusion of which two major art … Read more
1. The Mughal School of Painting developed as a fusion of which two major art … Read more - The Six Limbs of Indian Painting (Shadangas)
 In ancient India, the foundation of all visual art—especially painting—was based on six essential principles … Read more
In ancient India, the foundation of all visual art—especially painting—was based on six essential principles … Read more - Which Mughal emperor discouraged figurative painting?
 Aurangzeb (r. 1658–1707) was the Mughal emperor who discouraged figurative painting. In 1680, Aurangzeb banned … Read more
Aurangzeb (r. 1658–1707) was the Mughal emperor who discouraged figurative painting. In 1680, Aurangzeb banned … Read more - Mughal school of painting
 The Mughal school of painting represents one of the most sophisticated and influential artistic traditions … Read more
The Mughal school of painting represents one of the most sophisticated and influential artistic traditions … Read more - Realism vs. Abstract Art | Quiz
 Realism vs. Abstract Art Quiz Restart Quiz let currentQuestion = 0; let score = 0; … Read more
Realism vs. Abstract Art Quiz Restart Quiz let currentQuestion = 0; let score = 0; … Read more - The Art of Minimalism | Quiz
 The Art of Minimalism Quiz Restart Quiz let currentQuestion = 0; let score = 0; … Read more
The Art of Minimalism Quiz Restart Quiz let currentQuestion = 0; let score = 0; … Read more - Traditional Art Quiz
 Traditional Art Quiz Restart Quiz let currentQuestion = 0; let score = 0; const quizContainer … Read more
Traditional Art Quiz Restart Quiz let currentQuestion = 0; let score = 0; const quizContainer … Read more - Historical Art Quiz
 Historical Art Quiz Restart Quiz let currentQuestion = 0; let score = 0; const quizContainer … Read more
Historical Art Quiz Restart Quiz let currentQuestion = 0; let score = 0; const quizContainer … Read more - How Art Reflects Society and Culture Quiz
 How Art Reflects Society and Culture Quiz Restart Quiz let currentQuestion = 0; let score … Read more
How Art Reflects Society and Culture Quiz Restart Quiz let currentQuestion = 0; let score … Read more - The Role of Art in Mental Health and Therapy Quiz
 The Role of Art in Mental Health and Therapy Quiz Restart Quiz let currentQuestion = … Read more
The Role of Art in Mental Health and Therapy Quiz Restart Quiz let currentQuestion = … Read more - Gaming Characters Quiz
 Gaming Characters Quiz Restart Quiz let currentQuestion = 0; let score = 0; const quizContainer … Read more
Gaming Characters Quiz Restart Quiz let currentQuestion = 0; let score = 0; const quizContainer … Read more - Blox Fruits Quiz
 Blox Fruits Quiz Restart Quiz let currentQuestion = 0; let score = 0; const quizContainer … Read more
Blox Fruits Quiz Restart Quiz let currentQuestion = 0; let score = 0; const quizContainer … Read more - Solo Leveling Quiz
 Solo Leveling Quiz Restart Quiz let currentQuestion = 0; let score = 0; const quizContainer … Read more
Solo Leveling Quiz Restart Quiz let currentQuestion = 0; let score = 0; const quizContainer … Read more - How Well Do You Know Dragon Ball Z | Quiz
 Dragon Ball Z Quiz Restart Quiz let currentQuestion = 0; let score = 0; const … Read more
Dragon Ball Z Quiz Restart Quiz let currentQuestion = 0; let score = 0; const … Read more - Attack On Titan Quiz
 Attack on Titan Quiz Restart Quiz let currentQuestion = 0; let score = 0; const … Read more
Attack on Titan Quiz Restart Quiz let currentQuestion = 0; let score = 0; const … Read more - How Well Do You Know Naruto Uzumaki
 Naruto Quiz Restart Quiz let currentQuestion = 0; let score = 0; const quizContainer = … Read more
Naruto Quiz Restart Quiz let currentQuestion = 0; let score = 0; const quizContainer = … Read more - One Piece Quiz
 One Piece Quiz Restart Quiz let currentQuestion = 0; let score = 0; const quizContainer … Read more
One Piece Quiz Restart Quiz let currentQuestion = 0; let score = 0; const quizContainer … Read more - How Well Do You Know Amrita Sher-Gil?
 Question 1 Amrita Sher-Gil is known as:A) The Queen of Mughal ArtB) The Pioneer of … Read more
Question 1 Amrita Sher-Gil is known as:A) The Queen of Mughal ArtB) The Pioneer of … Read more - GK Quiz
 Modern Art Quiz Restart Quiz // Additional 15 questions on Modern Art { question: “Who … Read more
Modern Art Quiz Restart Quiz // Additional 15 questions on Modern Art { question: “Who … Read more - How Well Do You Know Amrita Sher-Gil?
 Quiz: How Well Do You Know Amrita Sher-Gil? Start Quiz Next Your Score: /20 Restart … Read more
Quiz: How Well Do You Know Amrita Sher-Gil? Start Quiz Next Your Score: /20 Restart … Read more - Blox Fruits Quiz
 Blox Fruits Quiz NEXT RESTART QUIZ let currentQuestion = 0; let score = 0; const … Read more
Blox Fruits Quiz NEXT RESTART QUIZ let currentQuestion = 0; let score = 0; const … Read more - Mine Craft Quiz
 Minecraft Quiz NEXT RESTART QUIZ NEXT: Mine Craft Quiz Can You Name These Iconic Actors?
Minecraft Quiz NEXT RESTART QUIZ NEXT: Mine Craft Quiz Can You Name These Iconic Actors? - Ajanta Cave Paintings (MCQs)
 100 multiple choice questions (MCQs) about Ajanta Cave Paintings, divided into categories 🏛️ General Information 🕰️ Historical Context 🖌️ Art … Read more
100 multiple choice questions (MCQs) about Ajanta Cave Paintings, divided into categories 🏛️ General Information 🕰️ Historical Context 🖌️ Art … Read more - Amar Nath Sehgal Biography, Childhood, Life, Artworks, Media, Awards, Exhibitions, Career + Legacy Guide + Top 15 Insights
 Amar Nath Sehgal (b. 1922) A philosopher, poet, artist and craftsman, Amar Nath Sehgal’s unique … Read more
Amar Nath Sehgal (b. 1922) A philosopher, poet, artist and craftsman, Amar Nath Sehgal’s unique … Read more - Anupam Sud’s Contribution to Women in Art
 Anupam Sud holds a unique and powerful place in the history of Indian art, particularly … Read more
Anupam Sud holds a unique and powerful place in the history of Indian art, particularly … Read more - Anupam Sud Biography: Untold Legacy & 15 Insightful Facts About the Iconic Printmaker
 Anupam Sud Biography explores the life, legacy, and powerful impact of one of India’s most … Read more
Anupam Sud Biography explores the life, legacy, and powerful impact of one of India’s most … Read more - Nandalal Bose Biography | Life, Paintings
 Nandalal Bose (1882-1966) Even as a young student at the Khudiram Bose’s Central Collegiate School, … Read more
Nandalal Bose (1882-1966) Even as a young student at the Khudiram Bose’s Central Collegiate School, … Read more - Anupam Sud Biography | Life, artworks
 Anupam Sud (b.1944) Anupam Sud, an outstanding graphist, has adopted printmaking, not only for artistic … Read more
Anupam Sud (b.1944) Anupam Sud, an outstanding graphist, has adopted printmaking, not only for artistic … Read more - Location Tracker App: Just Enter a Mobile Number and See Anyone’s Live Location—Right on Your Phone!
 Learn how to use Google Maps as a free Location Tracker App—no subscription, zero cost, … Read more
Learn how to use Google Maps as a free Location Tracker App—no subscription, zero cost, … Read more