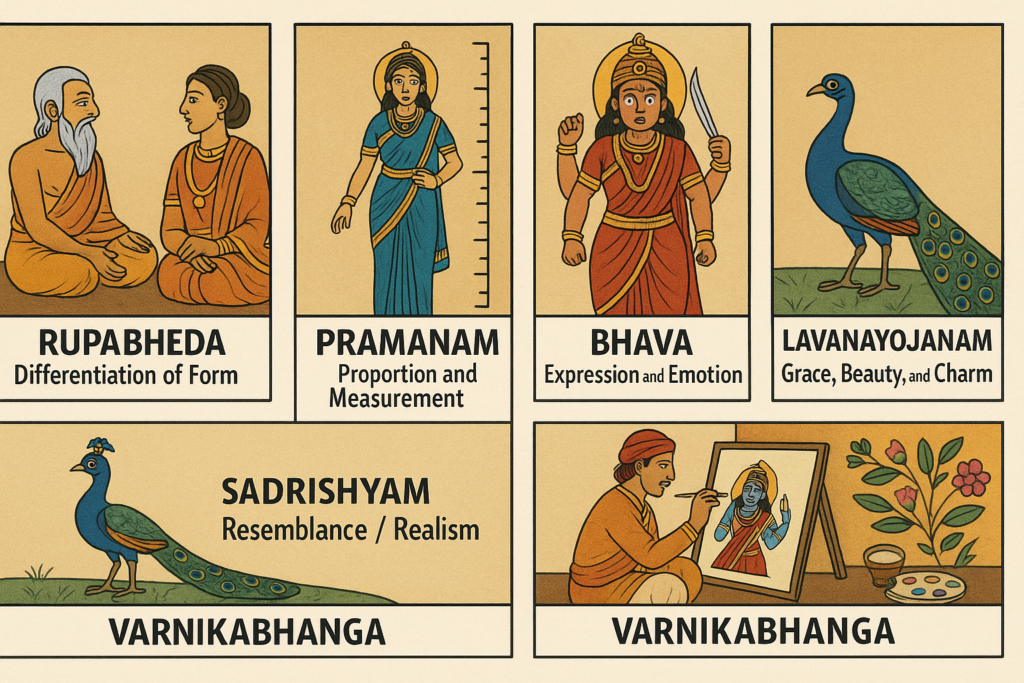
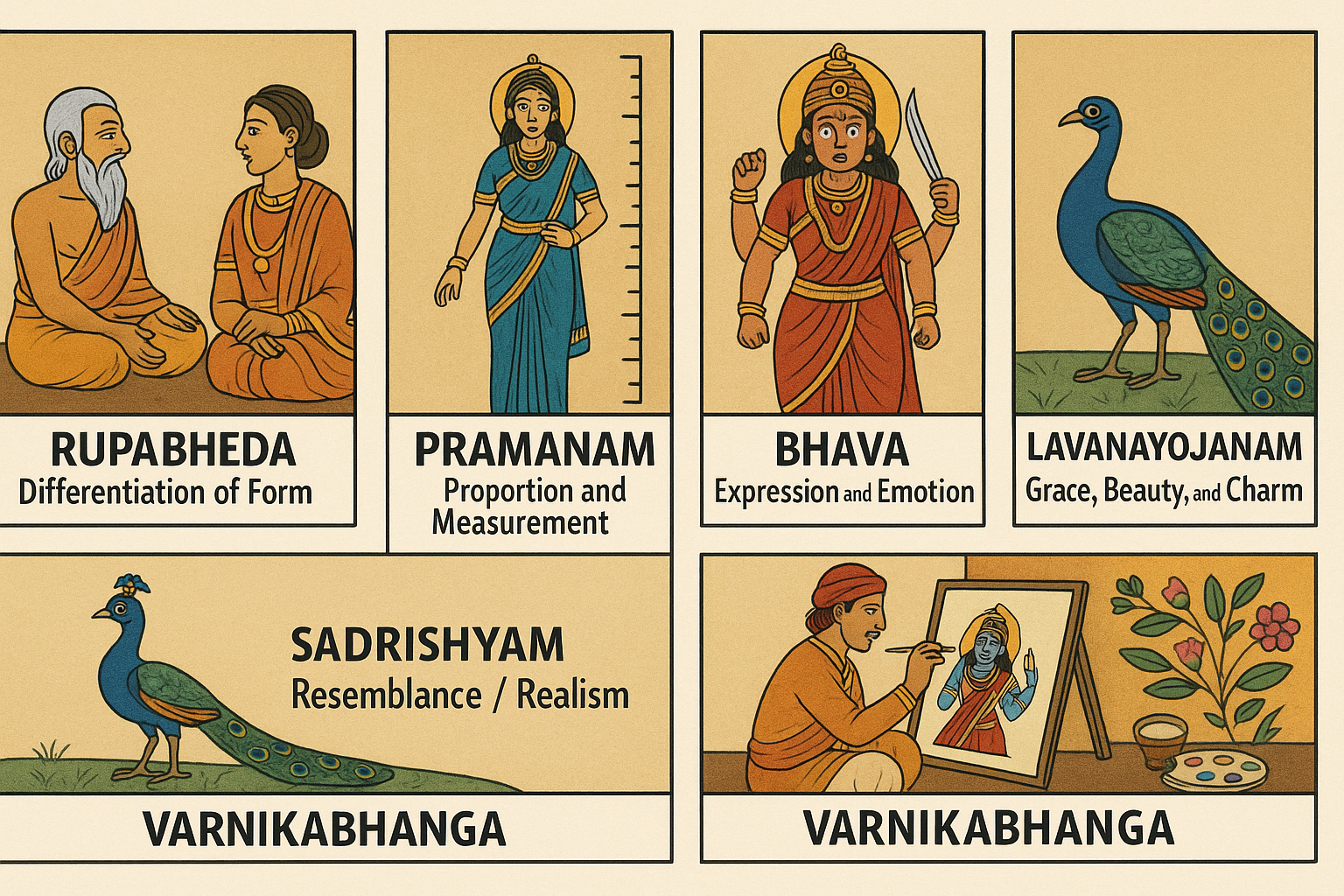
In ancient India, the foundation of all visual art—especially painting—was based on six essential principles described in classical Sanskrit texts. These are known as the Shadangas (ṣaḍ + aṅga = six + limbs).
These six limbs guided artists in technique, creativity, emotion, and beauty.
Table of Contents
1. Rupabheda (रूपभेद) – Differentiation of Form
This refers to understanding the distinct forms of objects, figures, and beings.
Artists must know how to show differences in shape, proportions, features, age, gender, and personality.
Example:
How a king looks different from a sage, or a child from an adult.
2. Pramanam (प्रमाणम्) – Proportion and Measurement
This principle focuses on accurate proportions, geometry, symmetry, and measurement.
Human body ratios, architectural precision, and balanced composition all fall under this limb.
Example:
Classical Indian art often uses ideal body measurements described in texts.
3. Bhava (भाव) – Expression and Emotion
Bhava is the ability to express emotion, mood, and story through painting.
It brings life into the artwork—making characters appear joyful, angry, divine, peaceful, or heroic.
Example:
The gentle smile of Buddha or the fierce expression of Goddess Durga.
4. Lavanayojanam (लावण्य-योजनम्) – Grace, Beauty, and Charm
This limb refers to creating aesthetic beauty—the gracefulness of posture, harmony of forms, and elegance of the painting.
Example:
Smooth flowing lines, pleasing curves, and decorative details.
5. Sadrishyam (सदृश्यम्) – Resemblance / Realism
The painting should have a true resemblance to the subject, even in a stylized form.
This includes likeness, accuracy, and identity.
Example:
A painted peacock must look clearly like a peacock, even if stylized.
6. Varnikabhanga (वर्णिकाभंग) – Use of Color and Technique
This refers to the knowledge of color, mixing, shading, brushwork, and application techniques.
Includes understanding pigments, color harmony, and texture.
Example:
Using natural pigments, appropriate contrasts, and smooth blending.
Summary Table
| Limb (Sanskrit) | Meaning | Focus Area |
|---|---|---|
| Rupabheda | Differentiation of forms | Identity, form, characteristics |
| Pramanam | Proportion | Measurement, balance, ideal ratios |
| Bhava | Emotion | Expression, storytelling |
| Lavanayojanam | Grace | Beauty, elegance, harmony |
| Sadrishyam | Resemblance | Realism, likeness |
| Varnikabhanga | Color application | Pigments, shading, technique |
MCQs – Six Limbs of Indian Painting
1. The term “Shadanga” refers to:
A. Six types of colors
B. Six limbs of Indian painting
C. Six artists of the Gupta period
D. Six schools of miniature painting
Answer: B
2. The Six Limbs of Painting were first mentioned in which ancient text?
A. Natyashastra
B. Vishnudharmottara Purana
C. Chitrasutra of the Vishnudharmottara
D. Arthashastra
Answer: C
3. Which limb of painting refers to “differentiation of forms”?
A. Bhava
B. Rupabheda
C. Pramanam
D. Sadrishyam
Answer: B
4. “Pramanam” deals with:
A. Measurement and proportion
B. Use of colors
C. Emotions
D. Likeness to nature
Answer: A
5. Bhava in painting refers to:
A. Color harmony
B. Emotional expression
C. Perfect proportions
D. Line quality
Answer: B
6. “Lavanayojanam” focuses mainly on:
A. Decoration
B. Grace and beauty
C. Optical illusion
D. Texture
Answer: B
7. Which limb ensures likeness to the real subject?
A. Sadrishyam
B. Varnikabhanga
C. Rupabheda
D. Lavanayojanam
Answer: A
8. “Varnikabhanga” is associated with:
A. Composition
B. Use of colors and techniques
C. Facial expressions
D. Subject matter
Answer: B
9. Which Shadanga limb deals with physical attributes and identity of figures?
A. Rupabheda
B. Bhava
C. Pramanam
D. Sadrishyam
Answer: A
10. The limb responsible for the aesthetic charm of a painting is:
A. Pramanam
B. Lavanayojanam
C. Sadrishyam
D. Varnikabhanga
Answer: B
11. Which principle relates to correct measurement according to ancient Indian texts?
A. Pramanam
B. Rupabheda
C. Bhava
D. Sadrishyam
Answer: A
12. Which limb helps an artist create realistic resemblance?
A. Bhava
B. Rupabheda
C. Sadrishyam
D. Pramanam
Answer: C
13. Applying natural pigments and mastering brushwork falls under:
A. Rupabheda
B. Varnikabhanga
C. Bhava
D. Lavanayojanam
Answer: B
14. The Shadanga system belongs to which period?
A. Medieval period
B. Gupta period
C. Ancient period
D. Mughal period
Answer: C
15. The purpose of “Bhava” is to:
A. Show contrast in colors
B. Convey mood and emotion
C. Establish measurement
D. Show resemblance
Answer: B
16. The limb that emphasizes beauty of form and elegance is:
A. Lavanayojanam
B. Pramanam
C. Bhava
D. Varnikabhanga
Answer: A
17. The concept of Six Limbs is connected to the discipline of:
A. Sculpture
B. Architecture
C. Painting
D. Calligraphy
Answer: C
18. “Differentiation of forms” involves understanding:
A. Anatomy and identity
B. Brush techniques
C. Color harmony
D. Ornamentation
Answer: A
19. The accurate depiction of emotions in a painting falls under:
A. Pramanam
B. Lavanayojanam
C. Bhava
D. Sadrishyam
Answer: C
20. The term “Sadrishyam” ensures:
A. Similarity and realism
B. Depth and shading
C. Symbolism
D. Line drawing
Answer: A
21. Use of bold lines, gentle curves, and graceful forms relates to:
A. Rupabheda
B. Lavanayojanam
C. Sadrishyam
D. Bhava
Answer: B
22. The limb that guides artists in shade, tone, and pigment application is:
A. Varnikabhanga
B. Pramanam
C. Bhava
D. Rupabheda
Answer: A
23. Which limb ensures that a painting “looks like” what it represents?
A. Bhava
B. Sadrishyam
C. Lavanayojanam
D. Rupabheda
Answer: B
24. Correct representation of human figure proportions comes under:
A. Pramanam
B. Varnikabhanga
C. Bhava
D. Sadrishyam
Answer: A
25. Which limb helps an artist maintain stylistic beauty and charm?
A. Lavanayojanam
B. Rupabheda
C. Pramanam
D. Sadrishyam
Answer: A